The way in which leave is processed depends on the leave settings setup under 'Global Defaults'.
It is possible to refine how the different leave types:
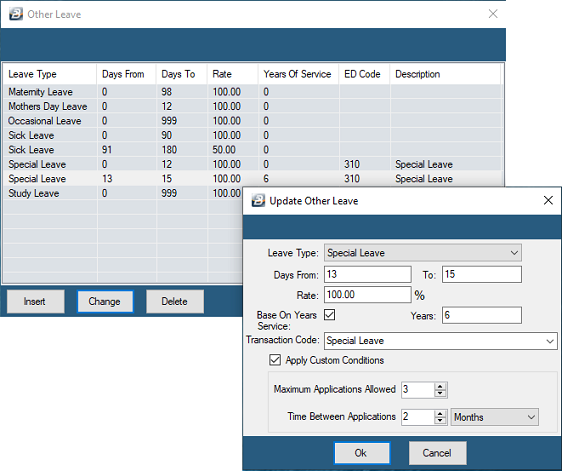
Use the 'Insert' and 'Change' buttons (see keyboard conventions) to enter, or update the other leave parameters.
• |
Have different leave conditions based on years service |
• |
Apply different leave rates beyond specified limits |
• |
Value leave days based on basic pay plus selected allowances |
 I
I
In the above example other leave types have been set up as follows:
Entitlement: 12 days paid at 100%. Belina PayrollHR gives the option to increase the parameters to have entitlement take into account years service. The compassionate leave entitlement is enshrined in Section 14B of the Labour Act Chapter 28:01 where it says: Employee's are entitled to twelve (12) days Special Leave each calendar year where the employee: - has been in contact with an infectious disease and is required to be absent from duty on the instruction of a medical practitioner - has been subpoenaed to attend court as a witness - attends a meeting as a delegate or office bearer of the registered trade union for the industry in which he/ she is employed - is detailed by police for questioning - suffers the death of a spouse, parent, child or legal dependant - has a justifiable compassionate ground |
|
Entitlement: 98 days paid at 100% Extract - Labour Act Chapter 28:01 Maternity leave (1) Unless more favourable conditions have otherwise been provided for in any employment contract or in any enactment, maternity leave shall be granted in terms of this section for a period of ninety-eight days on full pay to a female employee who has served for at least one year. [Subsection as amended by section 10 of Act 7 of 2005] (2) On production of a certificate signed by a registered medical practitioner or State Registered Nurse certifying that she is pregnant, a female employee may proceed on maternity leave not earlier than the forty-fifth day and not later than the twenty-first day prior to the expected date of delivery. (3) A female employee shall be entitled to be granted a maximum of three periods of maternity leave with respect to her total service to any one employer during which she shall be paid her full salary: Provided that paid maternity leave shall be granted only once during any period of twenty-four months calculated from the day any previous maternity leave was granted. (4) ….. [Subsection repealed by section 10 of Act 7 of 2005] (5) Any maternity leave requested in excess of the limits prescribed in this section may be granted as unpaid maternity leave. (6) Unless the employer grants sick leave for medical reasons other than maternity, sick leave may not be granted once paid maternity leave has begun or during a period of unpaid maternity leave. (7) During the period when a female employee is on maternity leave in accordance with this section, her normal benefits and entitlements, including her rights to seniority or advancement and the accumulation of pension rights, shall continue uninterrupted in the manner in which they would have continued had she not gone on such leave, and her period of service shall not be considered as having been interrupted, reduced or broken by the exercise of her right to maternity leave in terms of this section. (8) A female employee who is the mother of a suckling child shall, during each working day, be granted at her request at least one hour or two half-hour periods, as she may choose during normal working hours, for the purpose of nursing her child, and such employee may combine the portion or portions of time to which she is so entitled with any other normal breaks so as to constitute longer periods that she may find necessary or convenient for the purpose of nursing her child. (9) Any person who contravenes this section shall be guilty of an unfair labour practice. (10) Notwithstanding subsections (8) and (9), the grant of breaks during normal working time to a female employee for the purpose of nursing her child shall be made in accordance with all the exigencies of her employment and nothing done to prevent any disruption of normal production processes or any interference with the efficient running of an undertaking or industry shall be held to be in contravention of subsection (8). (11) A female employee shall be entitled to the benefits under subsection (8) for the period during which she actually nurses her child or six months, whichever is the lesser." |
|
Entitlement: up to 90 days paid at 100% then up to 180 days paid at 50%.
The Labour Act Chapter 28:01 specifies employees are entitled to: - 90 calendar days sick leave at full pay, and - 90 calendar days at half pay each calendar year.
The spirit of the law is that employees are entitled to 3 months at full pay and 3 months at half pay so using the equivalent number of working days can be safely assumed. Leave shall be granted, at the request of the employee, supported by a certificate signed by a registered medical practitioner if the employee is prevented from attending his duties because of illness, injury or medical treatment. |
|
Special Leave : |
Entitlement: up to 12 days paid at 100% (this is the statutory entitlement). In the example we have shown that employees with 6 years of services are entitled to 15 days paid at 100% (this is not statutory entitlement but set up as an example) |
Study Leave : |
Enter the number of days available, for example from 'Days From' 0 and 'Days To' 5 for a 5 day entitlement. |
Belina PayrollHR allows the setup of various leave types, each with their own controlling parameters that can be changed when necessary.