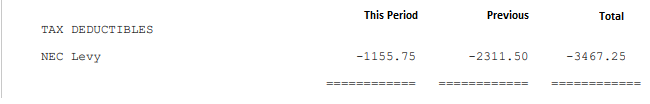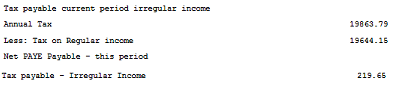The FDS Average method of calculating PAYE is another method of calculating the PAYE using the FDS tax balancing system. The FDS Forecast method is the default, and preferred, method to use.
Explanation
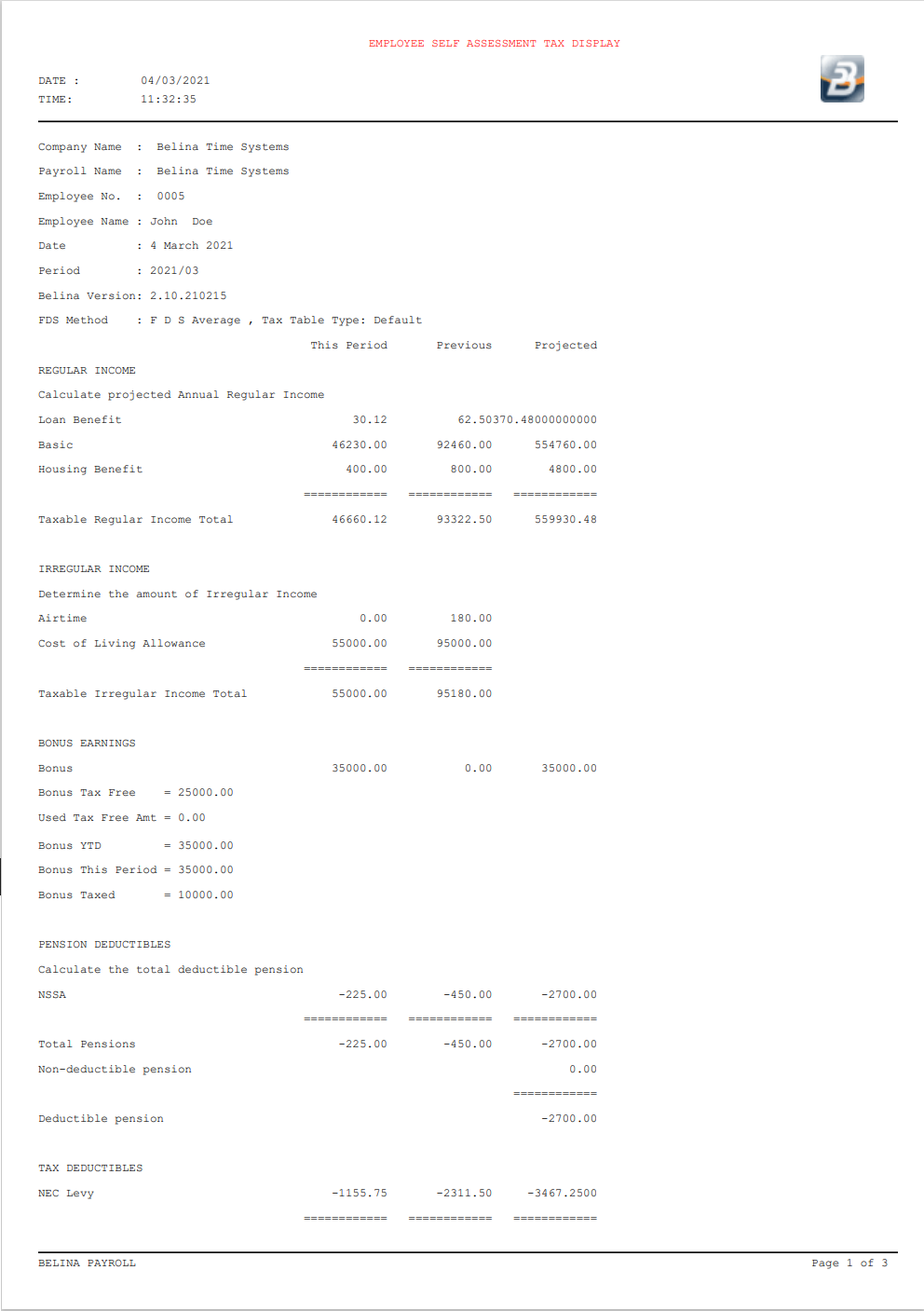
The 'Tax Display' shows how the PAYE amount has been calculated for an employee using the FDS Average Method of calculation
The 'Heading' section of the FDS - Forecast Average tax calculation displays:
|
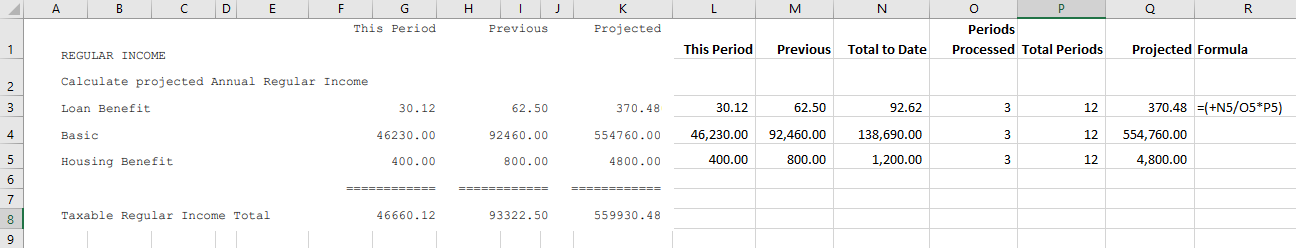
The projection of income includes: •the projection of Regular income •the inclusion of Irregular income •Bonus Earnings •Pension Deductibles
Regular Income The projection of regular income, in the FDS - Average Method of tax calculation, is done in the following manner for each Transaction Code:
|
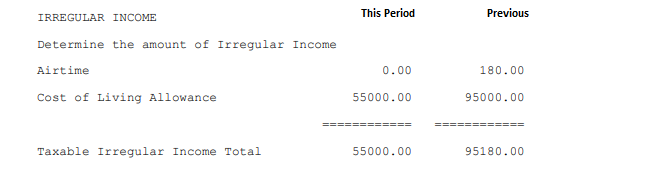
Irregular income is not projected. It is simply listed showing two totals. The total for 'This Period' and the total for 'Previous' period/s. These totals are used later in the calculation of PAYE. Tax on irregular income is calculated and deducted in the period in which it is earned. You will notice later that we calculate the tax related to irregular earnings in a two step process: •by calculating the tax on earnings to date excluding current period irregular earnings, then by •calculating the tax on earnings to date including current period irregular earnings •by subtracting the answers of the two, above, the tax on the current period irregular earnings will have been computed.
|
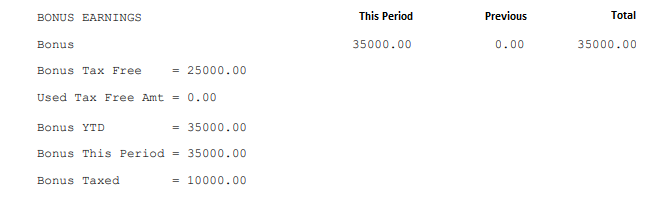
The Bonus section of the FDS - Average Method tax calculation displays:
|
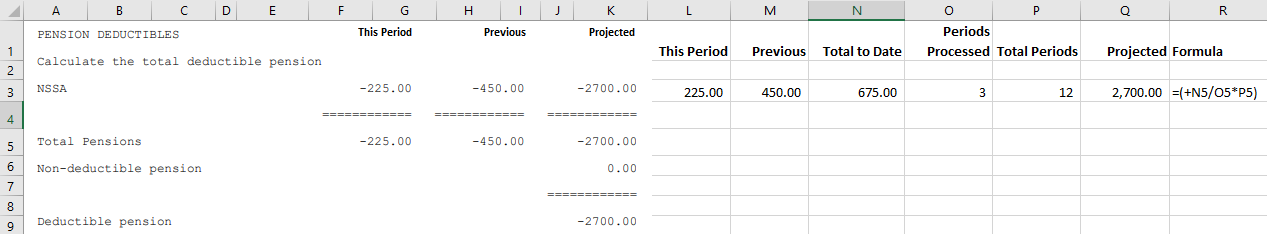
The Pension section of the FDS - Average Method tax calculation displays a listing of pension Transaction Codes that have transactions:
The table shows the Pension fund, the contribution 'This Period' and the contributions made in prior period/s, 'Previous' together with a 'Projection' of the total contribution for the year. The 2013 maximum pension deductible amount is $5400 or 7.5% of earnings which translates to $450 per month. The 'Deductible Pension' amount will be limited to these amounts. |
|
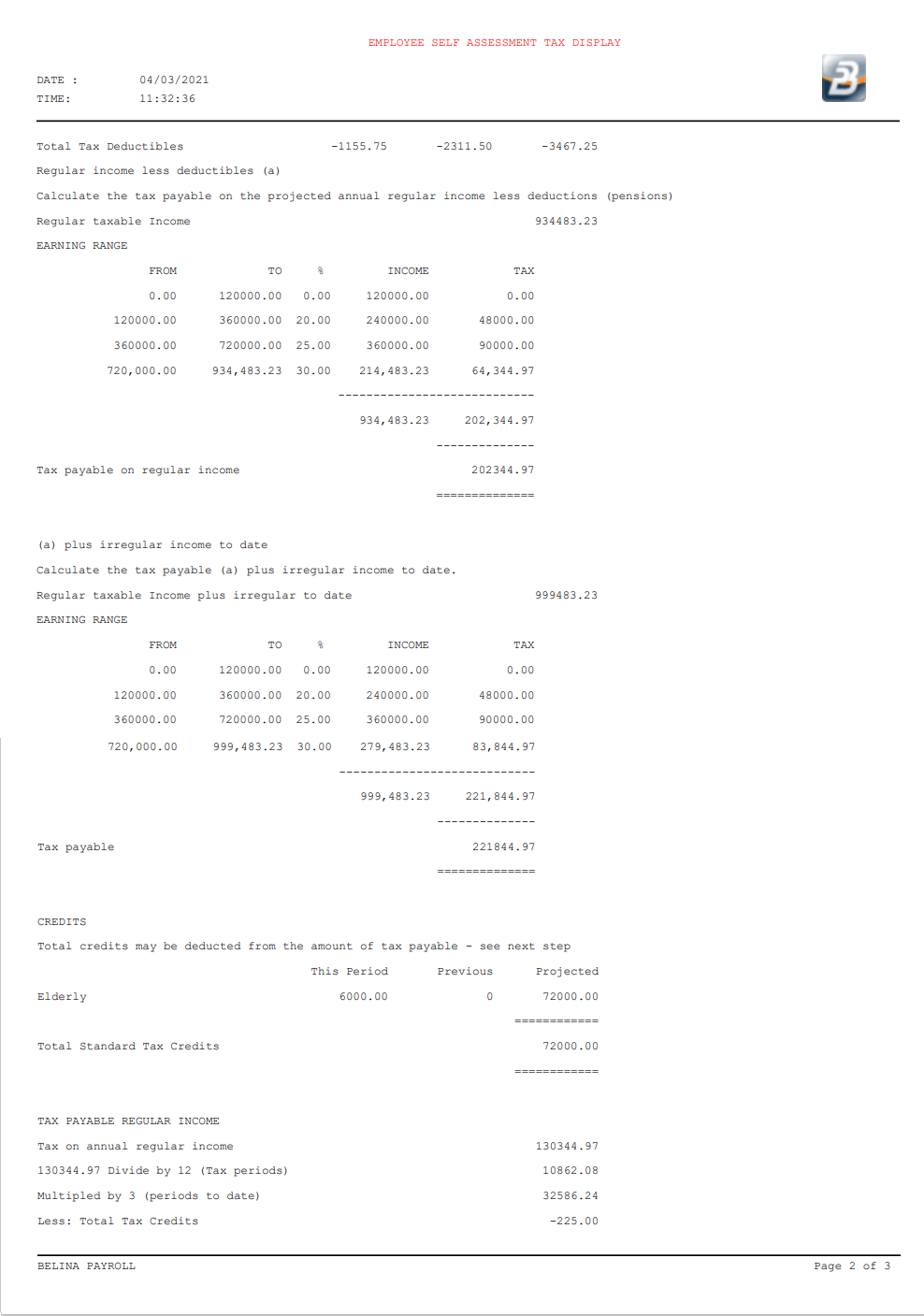
![]() Tax Payable on Projected Income
Tax Payable on Projected Income
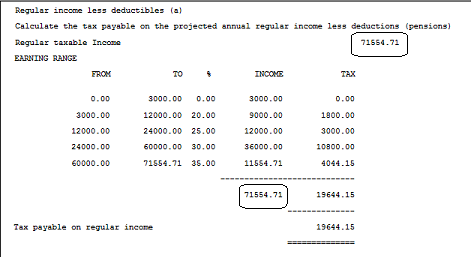
Step 1 - Calculate Net Projected Regular Income (including known irregular income up to but excluding the current period)
Step 2 Calculate the Tax Payable on Regular income Calculated in Step 1
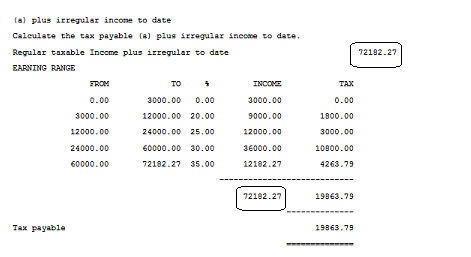
Step 3 - Calculate the Tax Payable on Regular income plus current period Irregular Income
Step 4 - We now calculate the tax payable on Regular Income for the current period
To narrate the above steps:
Step 5 - Calculate the tax payable on the Irregular income earned this period
Take the 'Tax payable' on Regular plus Irregular income, calculated in Step 3 and subtract the 'Tax Payable on regular income', calculated in Step 2. The result is the amount of taxation due on irregular income for the period, since tax on irregular earnings is calculated and paid in the period in which it is earned.
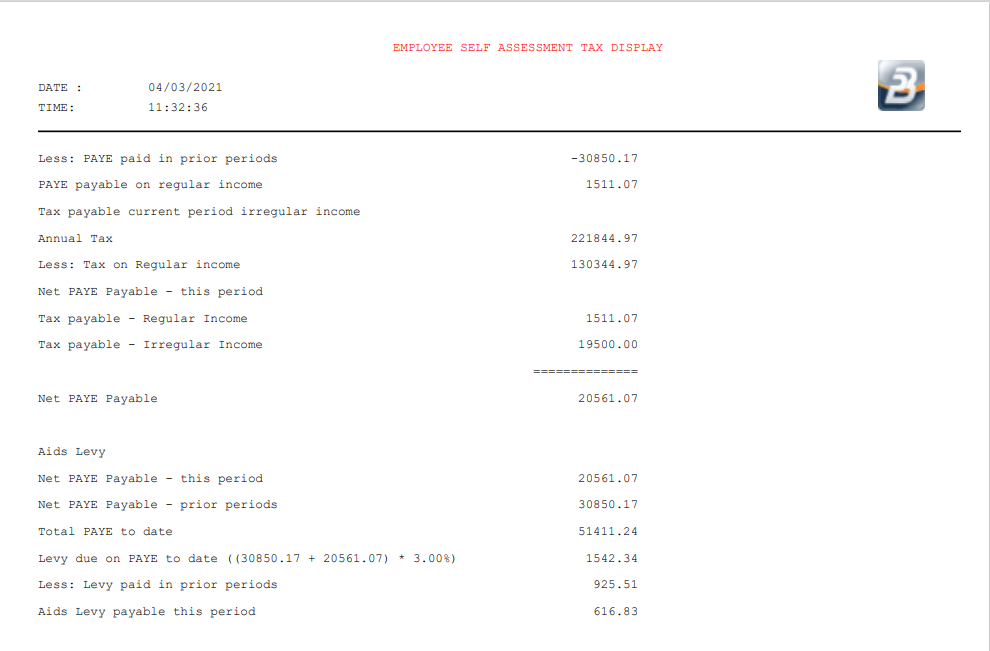
Step 6 - Tax Payable The total Tax Payable is the total of:
Step 7 - Aids Levy The final step in the calculation is to deal with the Aids Levy. The calculation looks at the amount of Aids Levy that should have been paid to date on 'PAYE to date' ($6767.70 x 3% = $203.03) less what has already been paid ($144.75) which leave $58.28 outstanding to be paid in the current period.
This is then added to the amount of tax payable on Income (Step 6) to give a Total Tax payable this period.
|